Interests Areas
- Health Care
- ESG
- Urban Planning
Projects
PINN for ECG Signal Denoising
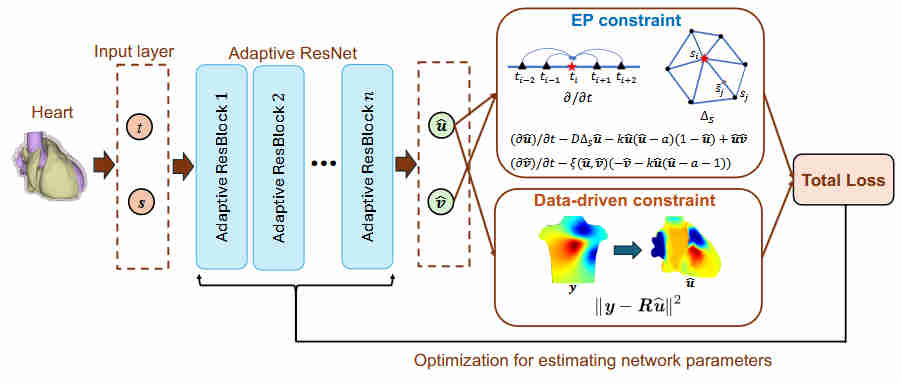
In this study, we propose EAND-ARN, a novel Electrophysiology-Aware Adaptive ResNet enhanced by numerical differentiation to address the inverse ECG problem.
ECG imaging (ECGI) aims to non-invasively reconstruct heart surface potentials (HSP) from body surface potentials (BSPM), but the ill-posed nature of the problem makes it highly sensitive to measurement noise.
Our key contributions include:
- Numerical Differentiation for EP Constraints
Unlike automatic differentiation (AD), our approach explicitly computes spatial Laplacian and temporal derivatives, effectively incorporating electrophysiological (EP) priors to improve stability and accuracy. - Adaptive Residual Network (ARN)
We introduce trainable residual connections to optimize gradient flow, enabling deeper networks and mitigating initialization issues.
Results & Impact:
Extensive experiments show that EAND-ARN outperforms traditional methods (e.g., Tikhonov regularization, STRE, and prior deep learning models) across multiple noise levels. Our model achieves
✅ Lower Relative Error (RE)
✅ Lower Mean Squared Error (MSE)
✅ Higher Correlation (CC)
Particularly in complex cardiac regions, these findings demonstrate the clinical potential of EAND-ARN, offering a more reliable computational tool for cardiac electrophysiology research and arrhythmia diagnosis.
fMRI-fNIRS
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) are both neuroimaging techniques that measure changes in brain blood oxygenation. fNIRS is more portable and cost-effective than fMRI, but inferior spatial resolution and penetration depth. Applications: studying brain function in naturalistic environments, developmental and clinical populations, infants and toddlers.